Curiosities
Scientists develop alternative to 'injection', idea was inspired by octopuses
Advertisement
As a result, several scientists are exploring alternative methods of administering these substances. Jean-Christophe Leroux, a professor at ETH Zurich in Switzerland, has innovated by developing a new way of administering injectable medications through the oral mucosa, using a patch applied to the inside of the cheek.
After a few unsuccessful attempts, Leroux and his team found inspiration in a living being: the octopus.
The design of the suction cup
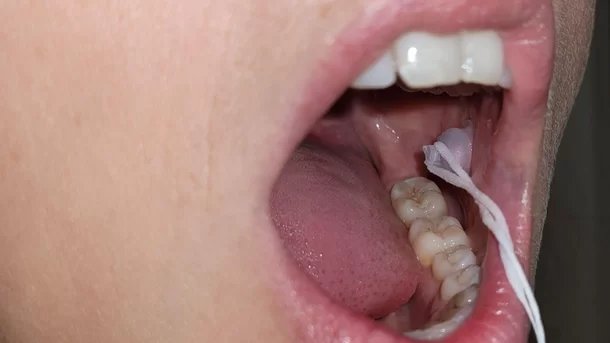
Scientists develop alternative to 'injection', idea was inspired by octopuses
In a study published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, Leroux and his team presented the prototype of the device they created, manufactured with the help of a 3D printer. This device resembles a flexible suction cup, attached to the inside of the patient's mouth.
They then conducted a test with volunteers and observed that the majority adapted very well to the new method, preferring it over injections.
According to the researcher, the aim is to create a more comfortable alternative to needles for administering certain medications. Leroux says: “We have developed an extremely simple and easy-to-use delivery system that could potentially replace injections for a variety of medications.”
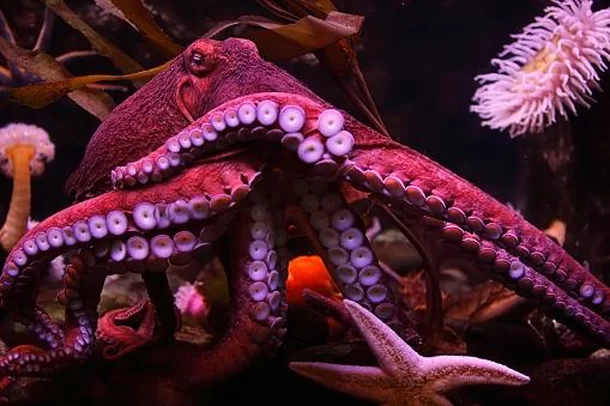
Inspiration from the octopus

Scientists develop alternative to 'injection', idea was inspired by octopuses10
Jean-Christophe Leroux explains that the inspiration came from the octopuses’ ability to anchor themselves in turbulent marine environments. “Our starting point was to imitate the excellent grip of these creatures on wet surfaces,” Leroux explains.
The suction cup technique has advantages over taking pills, as it allows the medication to be administered over time and can be removed when necessary. In addition, it prevents the medication from being dissolved by saliva.
After testing on dogs using the suction cup, it was observed that the animals had higher levels of the drug in their blood compared to conventional oral administration. Leroux comments: “We were genuinely impressed by the level of absorption achieved with such a simple system.”
However, it was noted that, in animals, the injectable method was still more efficient than the suction cup. Even so, the researchers emphasize that the prototype provided greater comfort to the animals, remaining applied to their cheeks for up to three hours without causing problems.
The scientists intend to further explore the use of the oral mucosa for drug administration, especially in the case of peptides, structures formed by the linking of two or more amino acid molecules. This could be particularly beneficial for people who require continuous injectable medications.
The expectation is that, over time, new methods that avoid the use of needles may be approved by regulatory agencies. According to the research conducted by Jean-Christophe Leroux's team, 75% of the forty volunteers who participated in the experiment stated that they did not feel discomfort with the suction cup. Approximately 83% expressed a preference for using this adhesive instead of the needle.
You may also like

Apps to discover ancestors: best options
Find your roots with the best apps for discovering ancestors, exploring family trees and historical records.
Keep Reading
McDonald's continues hiring at an average of US$$11/hour – understand
Accessible routine and easy entry continue to make McDonald's one of the most sought-after gateways in the US.
Keep Reading


